
Smart Ways to Optimize Your Chimpanzee Diet for Improved Health in 2025
Smart Ways to Optimize Your Chimpanzee Diet for Improved Health in 2025
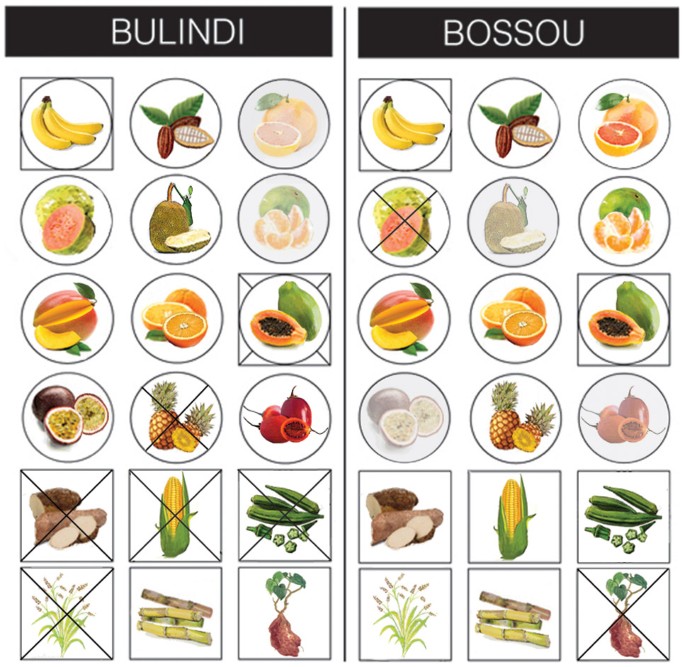

Understanding Chimpanzee Nutrition
The concept of chimpanzee nutrition is crucial when discussing the optimal diet for these fascinating primates. A typical chimpanzee diet consists predominantly of fruits, leaves, seeds, nuts, and occasionally insects, showcasing a varied and balanced approach to their dietary intake. By optimizing their food choices, we can enhance their health and well-being significantly. This article explores best practices, seasonal food availabilities, and the nutritional value of different dietary components relevant to chimpanzees.
The Role of Fruits in Chimpanzee Diet
Fruits are essential in the chimpanzee diet, providing critical vitamins, minerals, and energy. The nutritional value of fruits comes from their high content of carbohydrates, which serve as primary energy sources. Various fruits such as bananas, mangoes, and figs not only satisfy the sweet tooth of chimpanzees but also offer essential micronutrients when consumed in moderation. Understanding which fruits are available in different seasonal diets helps caregivers and researchers optimize chimpanzee food intake in both wild and captive settings. For example, providing seasonal fruits can significantly enhance feeding behavior and overall nutrition.
Insects and Protein Sources for Chimpanzees
Although fruits are the most calorically dense component of the chimpanzee food supply, protein sources such as insects are equally important. Insects provide essential amino acids and support chimpanzee digestive system functioning, allowing them to thrive. Moreover, these protein-rich foods can affect health and reproductive success in chimpanzee populations. Integrating a variety of insects into their daily meals not only mimics their natural feeding behavior but also prevents nutritional deficiencies in monkeys surviving in controlled environments.
Diverse Dietary Habits of Chimpanzees
The dietary habits of chimpanzees vary significantly based on their habitat, availability of plant foods, and seasonal changes. Understanding the ecological balance can help improve their care in captive settings, whereby dietary diversity can enhance overall health. It is essential to examine chimpanzee feeding patterns and the associated environmental factors that contribute to changes in their food choices over time.
Feeding Ecology and Seasonal Food Availability
Food availability fluctuates with seasons, and chimpanzees exhibit unique foraging strategies to adapt to such changes. During scarce months, feeding habits may lean towards available nuts and seeds, while abundant fruit seasons lead to increased fruit consumption. Research on chimpanzee foraging behavior has shown that they strategically remember where to find concentrated patches of food. This memory aids foraging in competitive environments, proving their cognitive abilities extend beyond mere survival. Therefore, providing appropriate seasonal diets in captivity can greatly influence their overall health outcomes.
Nutrition and Behavioral Ecology
Understanding chimpanzees’ behavioral ecology also helps comprehend their dietary needs. Groups often forage together, reflecting social structures that influence their dietary choices. Such cooperative strategies not only enhance feeding efficiency but also foster social connections. By incorporating a mix of foods tailored to group dynamics, chimpanzee caregivers can better simulate natural conditions and improve the animals’ health. Successful integration of varied foods accounts for both nutritional needs and social aspects, creating a harmonious feeding environment.
Health Benefits of Chimpanzee Diet
Optimizing a plant-based diet for chimpanzees leads to numerous health benefits, both physical and psychological. Regular intake of diverse foods can mitigate risks for diseases prevalent in captive scenarios, such as obesity and related health issues. By ensuring adequate energy requirements of chimpanzees, caregivers can promote better physical health and promote behaviors indicative of well-being.
Identifying Nutritional Deficiencies
It is vital to monitor and address any nutritional deficiencies in chimpanzees. Analyses reveal varying levels of important macronutrients and micronutrients across food types. Regular screening can help assess the necessity for dietary adjustments and potential supplements. Identifying signs of deficiency early can lead to faster resolution through dietary changes or enrichment strategies.
Macronutrients and Micronutrients in Chimpanzee Diet
Adequately balancing the macronutrients in chimpanzee diets is crucial for their overall health. Understanding the ratio of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates allows for calculated meals tailored to each individual’s needs. Additionally, ensuring a sufficient intake of micronutrients can enhance their health and lifespan, making informed dietary choices a priority in managing their nutrition.
Feeding Enrichment and Change in Dietary Preferences
Feeding enrichment plays a fundamental role in maintaining a successful chimpanzee diet strategy, particularly in captivity. Programs focused on feeding innovation offer varied food preparation methods, ensuring stimulation while promoting nutritional intake. Daily changes in food presentation influence chimpanzee food choices and can lead to greater dietary diversity. Fostering exploration in their feeding practices is essential for maintaining interest and improving overall wellness.
Impact of Environment on Feeding Behavior
Environmental factors such as habitat degradation and human impact directly affect chimpanzee availability and influence their feeding behavior. Ongoing conservation efforts aim to address these issues, effectively supporting their needs in the wild. Minimal human interference promotes diverse food sources, enabling healthy feeding habits and reduces competition for food among chimpanzee populations.
Feeding Strategies for Captive Chimpanzees
Implementing effective feeding strategies for captive chimpanzees is pivotal for overall health. Strategies that mimic natural foraging techniques can empower chimpanzees to engage body and mind, alleviating stress and stimulating their physical and cognitive abilities. Caregivers can optimize artificial diets by including foods that align more closely with what chimpanzees eat in the wild. In adopting these strategies, their well-being can vastly improve, sustaining healthier lifestyles and promoting longevity.
Key Takeaways
- Chimpanzees thrive best with a varied diet rich in fruits, leaves, and protein sources.
- Seasonal availability directs dietary changes, which can be harnessed for optimal feeding practices.
- Nutritional deficiencies need regular monitoring to tailor diets effectively.
- Focus on feeding enrichment fosters better health and well-being.
- Adapting captive diets to include natural food options aligns with primate nutrition needs.
FAQ
1. What are the main components of a healthy chimpanzee diet?
A healthy chimpanzee diet primarily includes high-quality fruits, leafy greens, seeds, nuts, and insects. This diverse dietary intake is crucial for satisfying their nutritional intake, supporting overall health, and helping in energy requirements. Natural food choices are key for optimal chimpanzee health benefits, especially in their captive care settings.
2. How does habitat impact the chimpanzee diet?
Chimpanzee diet significantly varies based on their natural habitat. Factors such as available resources, seasonal fluctuations in fruit availability, and the presence of food competition shape their dietary preferences. As habitats change due to environmental impacts, the adaptability of their diet relies heavily on understanding access to essential food sources.
3. What role do insects play in the diet of chimpanzees?
Insects serve as a vital protein source in the diet of chimpanzees. They are nutrient-dense and contribute essential amino acids required for maintaining health and vitality. The consumption of insects complements the overall nutrient balance within their plant-based diets and is often a preferred food in natural feeding behavior.
4. How can captive feeding strategies improve chimpanzee health?
Implementing captive feeding strategies that mimic natural foraging encourages chimpanzees to engage in physical activities and cognitive challenges, which are crucial for their mental well-being. Offering diverse food types and presentation methods increases dietary variety, effectively addressing their behavioral ecology and bolstering overall chimpanzee welfare.
5. What challenges face the dietary practices of chimpanzees in the wild?
Challenges such as habitat destruction, human interference, and climate change impact chimpanzee food sources. These pressures can lead to limited access to nutritional varieties and heighten competition for available food. Understanding these challenges helps enhance conservation efforts aimed at sustaining healthy chimpanzee populations and ecosystems.