Essential Guide to Gastroparesis Diet: Practical Foods for Effective Management in 2025
Essential Guide to Gastroparesis Diet: Practical Foods for Effective Management in 2025
Understanding Gastroparesis and Its Dietary Needs
Gastroparesis is a condition that affects the stomach’s ability to empty its contents, leading to various digestive issues. A **gastroparesis diet** is essential for managing symptoms and ensuring proper nutrient absorption. This condition often requires individuals to modify their food intake, primarily focusing on easy-to-digest foods, low-fiber diets, and high-calorie options. In this section, we will explore what gastroparesis is, the symptoms to watch for, and how dietary modifications can impact daily life.
What is Gastroparesis?
Gastroparesis is a form of delayed gastric emptying where the stomach takes too long to digest food. This can lead to symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, bloating, and abdominal pain. Common causes include diabetes, certain medications, and other underlying health conditions. Understanding these symptoms can help individuals identify when dietary alterations, like introducing **soft foods for gastroparesis**, are necessary. Managing gastroparesis involves monitoring food intake and adjusting diets to suit personal tolerances.
Symptoms of Gastroparesis
Recognizing the symptoms of gastroparesis is crucial for effective management. Symptoms often vary in intensity but may include early satiety, pain, and nausea after eating. It is advisable for individuals to keep a **food diary** documenting their eating habits and symptoms, as this can help identify which foods cause issues and which are friendly toward digestion. Such documentation is often instrumental in **meal planning** and finding the right balance that promotes better gut health.
Importance of Dietary Modifications
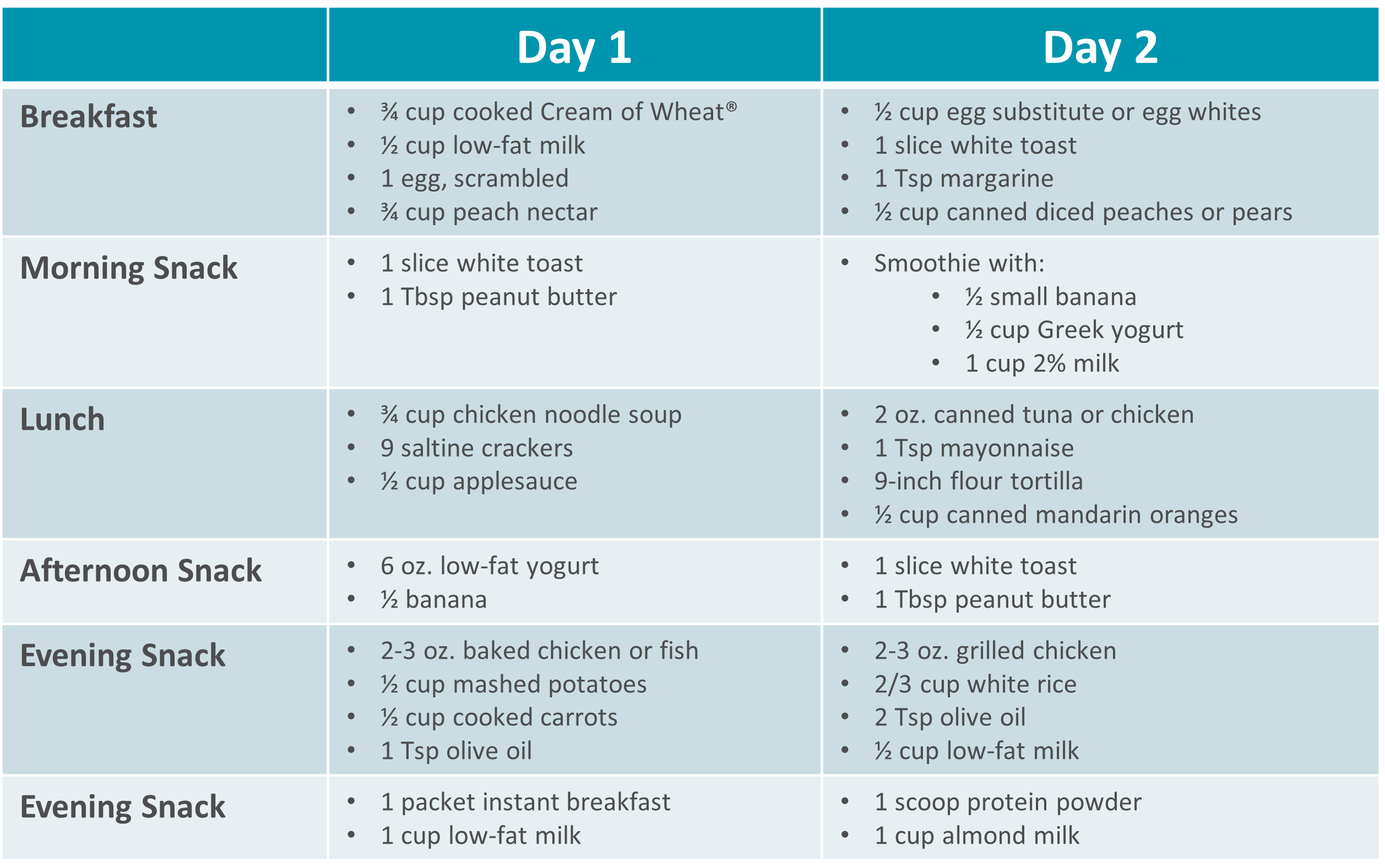
Changes to diet are vital for managing gastroparesis effectively. A **low-fiber diet**, focusing on easily digestible foods and smaller meal portions, can prevent overwhelming the stomach and reduce discomfort. Transitioning to a **high calorie diet** comprised of nutrient-dense options, such as **high protein sources** and **healthy fats**, can help maintain weight and support overall health. Moreover, **liquid nutrition** such as broth, juices, and snacks tailored to ease digestion can greatly complement solid meals.
Gastroparesis-Friendly Foods for Your Diet
Choosing suitable foods greatly impacts the comfort level for individuals with gastroparesis. There are several **gastroparesis-friendly foods** that can ensure not only enjoyment but also effective management of this condition. This section will detail specific food categories to incorporate into your diet.
Easy to Digest Foods
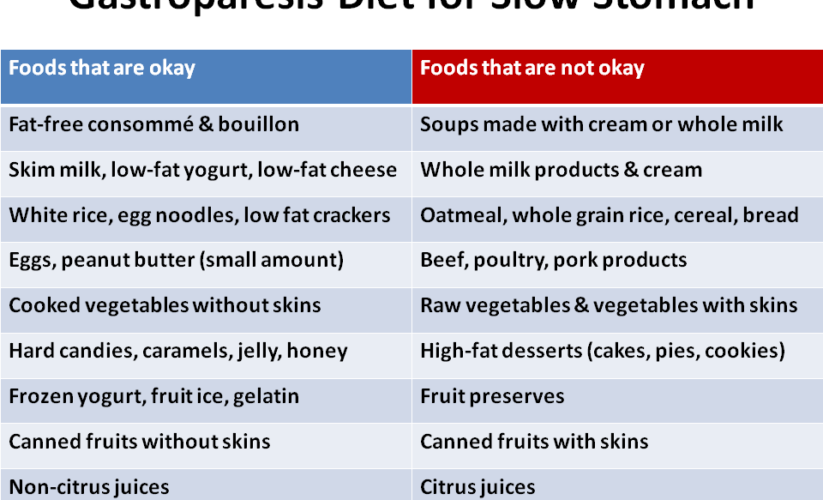
Foods that are **easy to digest** can make a significant difference for someone dealing with gastroparesis. Options such as white rice, boiled potatoes, and certain fruits, including bananas and applesauce are often well-tolerated. Incorporating **pureed foods** can also be beneficial. Cooking methods like boiling or steaming help preserve the food’s nutrients while making them easier to ingest. **Snacks options** such as veggie purees and smoothies can keep energy levels up without adding to discomfort.
High Calorie and Protein-Rich Selections
For individuals with gastroparesis, maintaining weight can be a persistent concern. Incorporating **high-calorie** and **high protein** foods is indispensable. Some examples include **protein shakes**, Greek yogurt, and skinless chicken. **Meal replacement** options provide another concentrated source of protein while being easy to take in. This emphasis on caloric density helps ensures that nutritional needs are met without overwhelming the stomach.
Bland and Low-Fat Foods
A **bland diet** is often recommended for those suffering from gastroparesis due to the reduced likelihood of triggering nausea or gastrointestinal discomfort. Foods like broths, grits, and soft casseroles can fit this description. Additionally, adhering to **low-fat meals** can facilitate digestion and improve overall comfort. Always **chew food well** and practice **eating slow** to support optimal digestion. Care should also be taken to **avoid high fat, high sugar foods** that may induce gastric distress.
Meal Planning and Preparation Tips
Successful management of gastroparesis hinges significantly on effective **meal planning** and understanding how to prepare meals thoughtfully. With the right strategies in place, individuals can enhance their meal experience dramatically, making dietary restrictions feel less burdensome.
Meal Frequency and Portion Control
Adopting a strategy that focuses on **meal frequency** can combat symptoms associated with gastroparesis. Rather than consuming three large meals a day, consider having five to six smaller meals spaced out throughout the day. This adjustment helps avoid overwhelming the digestive system. Additionally, employing **portion control** ensures each meal is modest. Using a **nutrition tracker** can aid in balancing meals accordingly.
Cooking Methods for Optimal Nutrition
Experimenting with various **cooking methods** can yield better-digested meals. Techniques such as steaming or baking, instead of frying, create lighter meals that are still enjoyable. With **food preservation** tips such as freezing small portions of cooked meals, one can have appropriate options readily available. Consider incorporating **vegetable juices** and fruit smoothies to hydrate and enhance nutrition without risking discomfort.
Shopping for Gastroparesis Diet
Grocery shopping under these dietary needs means prioritizing certain foods while avoiding triggers. It’s essential to always check **food labels** and minimize **chemical food additives**, which can provoke symptoms. Focus on **nutrient-dense foods**, opting for powders or beverages that are easy to digest. Understanding the layout of the grocery store can streamline your shopping, allowing for a healthier basket tailored to manage **digestive issues** effectively.
Long-Term Management Strategies
Effective management of a gastroparesis diet extends beyond meal choices and incorporates longer-term strategies. This section will explore practical strategies and **lifestyle changes** that can support overall digestive health.
Hydration Tips and Electrolyte Balance
Proper **hydration** is crucial when managing gastroparesis. Dehydration can exacerbate symptoms, so aim to consume fluids regularly, ideally through **low sodium foods** and electrolyte-rich options. Smoothies and broth contribute positively toward hydration while helping maintain a balanced electrolyte level. **Hydration choices** can be integrated into meal prep to make access convenient and support effective management.
Vitamin and Mineral Supplements
Incorporating **vitamin supplements** into your diet can offset any nutritional gaps caused by dietary restrictions. Consulting with a healthcare provider can lead to personalized recommendations focusing on **nutrient absorption** and **vitamin D sources** to bolster overall health. On a similar note, **probiotic foods** can play a vital role in supporting gut health, potentially alleviating some symptoms experienced with gastroparesis.
Seeking Professional Guidance
Partnering with a dietitian who understands the intricacies of a gastroparesis diet can be incredibly beneficial. They will provide specialized **dietitian recommendations** that ensure nutrient adequacy while considering individual preferences and sensitivities. Regular follow-up visits make navigating the dietary landscape smoother, aligning with **eating habits** that work effectively for individual needs.
Key Takeaways
- Individuals with gastroparesis benefit significantly from a **gastroparesis diet** that emphasizes low-fiber, low-fat, and **easy to digest foods**.
- Meal frequency plays an essential role—smaller, more frequent meals can alleviate discomfort.
- Staying adequately hydrated and maintaining an electrolyte balance is key to symptom management.
- Consulting with certified professionals can enhance diet management and nutrient adequacy.
- Creating a system for **meal prep ideas** allows for more convenient eating, especially considering **food sensitivities** and preferences.
FAQ
1. What should I include in my gastroparesis diet?
Your gastroparesis diet should consist of **gastroparesis-friendly foods**, focusing on low-fiber, high-calorie items that are easy to digest. Incorporate more **soft foods** and **high protein sources**, while also considering **liquid nutrition** options like soup or smoothies.
2. Can you recommend some good hydration strategies?
Proper hydration is crucial, especially when experiencing symptoms of gastroparesis. Consider drinking fluids that contain electrolytes, such as sports drinks or broth. **Fruit smoothies** and herbal teas are also excellent options for both hydration and nutrition.
3. How can I maintain nutrient absorption on a restrictive diet?
To maintain **nutrient absorption**, prioritize nutrient-dense foods and consult with a dietitian for **vitamin supplementation** if necessary. Incorporate **probiotic foods** to enhance gut health and digestion, and track your food intake with a **nutrition tracker**.
4. What role do meal replacements play in managing gastroparesis?
**Meal replacements** can provide concentrated nutrition without the effort of regular cooking, making them suitable for those who struggle with food intake due to gastroparesis. They can help ensure you meet your caloric and nutritional needs, particularly when appetite fluctuates.
5. Are there any specific foods to avoid with gastroparesis?
Avoid foods high in fat and sugar, as they can exacerbate symptoms. Also, refrain from **gas-inducing foods** like certain beans and cruciferous vegetables. Keep a **food diary** to identify personal triggers and customize your **dietary modifications** effectively.